Page
Last Updated:
Tuesday, 19 January 2016 11:02 EDT, © 2012, 2016
PROJECT: Model Metadata Ontology
Dr. Dean S. Hartley III
| Project Metadata |
Keywords |
|
Label |
Name |
Other |
Year |
DurationYrs |
|
Client |
Hartley
Consulting |
none
Commercial |
|
|
|
Dates |
|
|
2013 |
1 |
|
Employer |
Hartley
Consulting |
|
|
|
|
Partner |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
Classification issues |
|
Computer hardware issues |
|
Configuration management |
|
Consequence Management |
|
Data Verification & Validation |
|
Database design |
|
DIME/PMESII Modeling |
|
Documentation standards |
|
Geopolitical analysis |
|
Global War on Terrorism (GWOT) |
|
Human factors |
|
Human, Social, Cultural Behavior (HSCB) Modeling |
|
Impact analysis |
|
Independent Verification & Validation (IV&V) |
|
Information storage and retrieval |
|
Irregular Warfare (IW) |
|
Knowledge Management (KM) |
|
Metadata |
|
Model/System integration |
|
Modeling, Simulation & Gaming (MSG) |
|
Ontologies |
|
Operations Other Than War (OOTW) |
|
Software issues |
|
Software reuse |
|
Stability Operations (SASO, SSTR) |
|
Verification, Validation & Accreditation (VV&A) |
|
Warfare modeling |
|
Challenge:
Identify the characteristics of models of Irregular Warfare (IW) [and similar
domains] that are useful to potential users who are searching for the right
model to use. This is currently an Independent Research & Development (IR&D)
project.
Background:
Since at least the 1970s, the US government has developed
catalogs of models. Each catalog included metadata that the compilers
thought would be valuable in distinguishing the models and in determining which
models might be functional for some future user. A fair number of these
catalogs have been examined and the results were combined into categories with
entries representing actual models in the Department of Defense inventory.
These entries are known to be not comprehensive. For example, Wikipedia
has a list of computer programming languages that is much larger than the
entries in that category; however, some of these languages may be obsolete or
not useful for the types of models useful for IW. In general, this webpage
will be "under construction" for some time as additional entries are suggested
and incorporated.
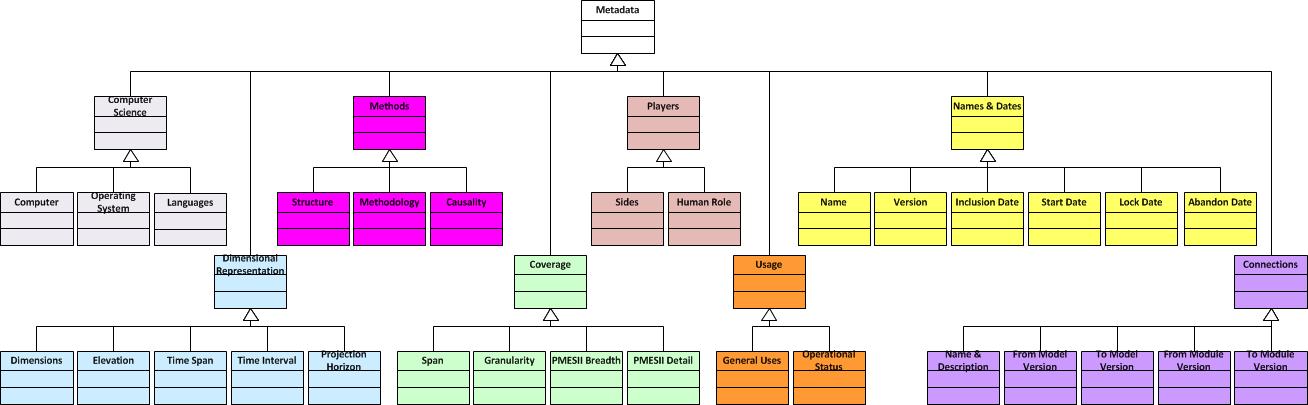
Upper Level Ontology:
The metadata ontology is a taxonomy at its highest levels. Eight
categories are needed: names & dates, computer science, methods, players, dimensional
representation, coverage, usage, and connections. These categories are subdivided as
shown in the figure below.
The subcategories are defined as follows:
- Names & Dates
- Name: the system, model, or module name.
- Version: the version identifier of the system, model, or
module.
- Inclusion Date: (for models and modules) the date the model
version was included in the system version or the module version was
included in the model version.
- Start Date: the date the system, model, or module version
was begun to be defined.
- Lock Date: the date the system, model, or module version
was completed. Any further changes would constitute a new version.
- Abandon Date: the date on which the system, model, or
module version is planned to be replaced by a new version or shelved.
- Computer Science
- Computer: the minimal computer hardware required, whether
laptop, cluster, supercomputer, etc.
- Operating Systems: the computer operating systems
alternatives.
- Languages: the computer languages used.
- Dimensional Representation
- Dimensions: the surface representation: none, some
type of 2-dimensional representation, some type of 1-dimensional representation.
- Elevation: the elevation/depth represention, if any.
- Time Span: the general length of time represented in a
model run, if any, e.g., days, months, years.
- Time Interval: the smallest time interval represented, if
any, e.g., hours, days, months.
- Projection Horizon: the length of time for projected
results, if any, units of time and numerical modifier.
- Methods
- Structure: the overall model methodology structure.
- Methodology: the methodology types employed.
- Causality: the type of causality, if any, used in the
model.
- Coverage
- Span: the geopolitical coverage, e.g., multinational,
sub-national region, single individual.
- Granularity: the basic smallest unit of measure.
(There may be smaller units for specialized sub-components as long as they
are minor elements of the model.)
- PMESII Breadth: the number of PMESII+ categories considered
relevant for the model as compared to the total number of PMESII+ categories
(currently 8: political, military, economic, social, information,
infrastructure, kinetic, and environment).
- PMESII Detail: based on the number of variable classes considered
relevant for the model, the total number of variable classes (currently
408), and the fraction of relevant categories. The total number of variable
classes is multiplied by the fraction of relevant categories. The
result is divided into the number of relevant variable classes to obtain a
number representing a fraction of the possible detail.
- Players
- Sides: the number of sides represented.
- Human Role: the type of role humans play in the model,
e.g., closed form, human-in-the-loop, etc.
- Usage
- General Uses: the various types of uses for which the model
is appropriate, includes the individual through strategic spectrum, the
acquisition, analysis, etc., classification, and more detailed usage types.
- Operational Status: the operational status, from conception
to being retired "to the shelf."
- Connections
- Name & Description: identification of the connection.
- From Model Version: identification of the model passing the
data.
- To Model Version: identification of the model receiving the
data.
- From Module Version: identification of the module passing
the data.
- To Module Version: identification of the module receiving
the data.
Lower Level Ontology:
Each subcategory has a set of descriptive classes. For all but four of
the subcategories, any given model is linked to a single class choice for each
subcategory. For the four remaining subcategories, the model may be linked
to a single class choice or to multiple class choices. These choices will
be augmented, as needed.
Names & Dates
- Name: single choice, free form input.
- Version: single choice, free form input.
- Inclusion Date: (for models and modules) single choice,
date input.
- Start Date: single choice, date input.
- Lock Date: single choice, date input.
- Abandon Date: single choice, date input.
Computer Science
- Computer: single choice.
- laptop
- desktop, heavy duty
- cluster, small
- cluster, large
- supercomputer
- Operating Systems: multiple choices.
- Windows
- Windows
- Windows XP
- Windows Vista
- Windows 7
- Unix
- Unix
- Linux
- GNU/Linux
- Red Hat Linux
- Ubuntu
- Mac
- Other
- Languages: multiple choices.
- None
- Artificial Intelligence Languages
- Database Languages
- Access
- Access VBA
- Access SQL
- dBase
- SQL
- SQL Server
- MySQL
- Oracle
- Sybase
- FoxPro
- Visual FoxPro
- Environment
- Adobe Flex
- CORBA
- Matlab
- .NET
- General Languages
- C
- FORTH
- FORTRAN
- Pascal
- PERL
- PL/I
- Visual Basic
- Graphics Languages
- Object Oriented Languages
- Ada
- C++
- C#
- Delphi
- Java
- Java Beans
- Javascript
- MODULA
- Python
- Smalltalk
- Other Languages
- Network Languages
- DyNet
- BayesNetToolbox
- Netica
- Simulation Languages
- ExtendSim
- FlexSim
- GPSS/H
- iThink
- MedModel
- MODSIM II
- PowerSim
- ProModel
- Ptolemy
- Pythagoras
- Repast
- SimEvents
- SIMAN
- Simscript
- Simula
- SimuLink
- SWARM
- VenSim
- Spreadsheet Languages
- Statistical Languages
- Web Languages
- ASPX
- Cold Fusion
- HTML
- TomCat
- XML
Dimensional Representation
- Dimensions: single choice.
- None
- 1 Dimensional
- 1D - corridor
- 1D x n corridors
- 2 Dimensional
- 2D - Triangle tiles
- 2D - Square tiles
- 2D - Hexagonal tiles
- 2D - Custom polygons
- 2D - Arc/Node network
- 2D - Arc/Node + tiles
- 2D - xy coords
- 2D - Arc/Nde + xy
- 2D - lat/long
- 2D - Arc/Node + lat/long
- Other
- Elevation: single choice.
- None
- Discrete
- Discrete - 1 level
- Discrete - 2 levels
- Discrete - 3 levels
- Continuous
- Plus Z - ground to air
- Orbital Z
- Z - subsurface to air
- Complete Z - subsurf, air, orbit
- Mixed
- Time Span: single choice.
- None
- Fractional Seconds
- Seconds
- Minutes
- Hours
- Days
- Weeks
- Months
- Years
- Mixed
- Time Interval: single choice.
- None
- Fractional Seconds
- Seconds
- Minutes
- Hours
- Days
- Weeks
- Months
- Years
- Mixed
- Projection Horizon: single choice of units, plus numerical
modifier.
- None
- Fractional Seconds
- Seconds
- Minutes
- Hours
- Days
- Weeks
- Months
- Years
- Mixed
Methods
- Structure: single choice.
- Unclear
- Data
- Data Collection, Automated
- Data Collection, Manual
- Data Collection, Semi-automated
- Database
- Environment
- Collaborative Environment
- Programming Environment
- Programming Environment, Agent Based
- Programming Environment, Object Oriented
- Programming Environment, Simulation
- Live Environment
- Virtual Environment
- Game
- Game, First Person
- Game, Manual
- Game, Massive Multiperson Online
- Wargame, Computer
- Wargame, Seminar
- Manual
- Checklist, Manual
- Checklist, Automated
- Conceptual Model
- Flowchart
- Network
- Bayes Net
- Influence Model/Decision Tree
- Network Model, Dynamic
- Network Model, Static
- Neural Net
- Petri Net
- Petri Net, Colored
- Other
- Algorithm
- Cognitive Architecture
- Decision Support System
- Expert System
- Optimizer
- Spreadsheet
- Static Model
- Web Page
- Simulation
- Simulation, Agent-Based (small agent)
- Simulation, Discrete Event
- Simulation, Object Oriented (large agent)
- Simulation, System Dynamics
- Simulation, Time-Stepped
- Simulation, Mixed
- Support
- Display System
- Graphical Tool
- Graphical User Interface
- Language/Text Parser
- Statistical Toolkit
- Support Model
- Support Module
- System
- System, HLA Confederation
- System, Loosely Coupled
- System, Tightly Coupled
- Methodology: multiple choices.
- Bayesian Analysis
- Bayesian Influence (static network)
- Bayesian network (dynamic)
- Data Methods
- Database
- Data fusion
- Data mining
- Distillation
- Realtime data connection
- Economic Methods
- Decision analysis
- Economic modeling
- Game theory
- General Equilibrium
- Optimization
- Linguistic Methods
- Language translators
- Linguistic analysis
- Media Analysis
- Meme analysis
- Natural Language Processing
- Text analysis
- Manual Methods
- Brainstorming
- Focus Groups
- Knowledge elicitation
- Polling/ Market Research
- Red Teaming
- Subject Matter Experts
- SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats)
- Network Methods
- Association matrix
- Influence diagram
- Network modeling
- Neural net
- Petri Nets
- Petri Nets, Colored
- Vulnerability / criticality analysis
- Other Methods
- Forensic Analysis
- Geographic Information System
- Graphical User Interface
- Methodologies vary with components
- Multi-user connectivity
- Ontology (relationships)
- Programming
- Pattern Methods
- Cluster analysis
- Pattern analysis
- Pattern recognition, complex data rendering (spatial and
temporal)
- Profiling
- Simulation
- Agent-based simulation
- Complex adaptive systems modeling
- Perturbation analysis
- Simulation
- Simulation - discrete event
- Simulation - system dynamics
- Simulation - time step
- Statistical Methods
- Diffusion model
- Discriminant analysis
- Forecasting
- Fuzzy sets
- Hidden Markov methods
- Regression
- Statistics
- Web Methods
- Webpage
- Webscraping techniques
- Causality: single choice.
- None
- Mixed
- Descriptive
- Inference
- Deterministic
- Statistical
- Stochastic
Coverage
- Span: single choice.
- N/A
- Global
- Supra-national
- National
- Regional
- Local
- Unit or group
- Individual
- Granularity: single choice.
- Not modeled
- Modeled at the global level
- Modeled at the supra-national level
- Modeled at the national level
- Modeled at the regional level
- Modeled at the local level
- Modeled at the unit or group level
- Modeled at the individual level
- PMESII Breadth: single choice, currently 1-8 of 8.
- PMESII Detail: single choice.
- Low Detail - below 26%
- Moderate Detail - 26% to 60%
- High Detail - 61% and up
Players
- Sides: single choice.
- N/A
- None
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- >9
- Implicit
- Mixed
- Human Role: single choice.
- Mixed
- ClosedForm
- Human-in-the-Loop
- Wargame/Game
- Virtual
- Live
Usage
- General Uses: multiple choices.
- Unspecified
- Spectrum of Operations
- N/A
- Strategic
- Operational
- Tactical
- Individual
- Community
- N/A
- Acquisition
- Analysis
- Education
- Experimentation
- Exploration
- Operations
- Planning
- Testing
- Training
- Operational Uses
- Impact Analysis
- 1.1 Real-Time Indicators & Warnings
- 1.2 Impact Model
- 1.3 Resource Simulation
- 1.4 Disaster and Other Special Impact
- 1.5 Crime Analysis
- 1.6 Narcotics Analysis
- 1.7 Terrorism Analysis
- 1.8 Insurgency Analysis
- Mission & Force Planning
- 2.1 Mission Definition
- 2.2 Task Analysis
- 2.3 Force Design
- 2.4 Logistics Analysis
- 2.5 Transport Analysis
- COA
- 3.1 COA Development
- 3.2 COA Comparison
- 3.3 MOE Calculator
- 3.4 Communications Analysis
- 3.5 Intel Ops
- 3.6 Public Affairs/Civil Affairs
- 3.7 PSYOP
- 3.8 Transition Planning
- Cost
- Situational Awareness
- 5.1 Situation Display
- 5.2 Data Warehouse
- 5.3 Control of models
- Combat
- Operational Status: single choice.
- Concept
- Design
- Implemented, Alpha
- Implemented, Beta
- Operational
- Phasing Out
- On the Shelf
Connections
- Name & Description: single choice.
- Name: free form input.
- Connection Type.
- Fully automatic:
no human
intervention required.
- Semi-authomatic:
all data must
be reformatted, but not interpreted by human intervention.
- Fully manual:
all data must
be reformatted and interpreted by human intervention.
- Unknown: not
known at that time.
- Connection Description: free form input
- From Model Version: single choice.
- Model Name: select from list.
- Model Version: select from list.
- To Model Version: single choice.
- Model Name: select from list.
- Model Version: select from list.
- From Module Version: single choice.
- Module Name: select from list.
- Module Version: select from list.
- To Module Version: single choice.
- Module Name: select from list.
- Module Version: select from list.
Conclusions:
This ontology represents a part of the description of any particular IW model
and of the set of IW models in general. It does not contain the detailed
description required to fully understand any model, as such a description
contains too many variable components. However, it does contain enough
information to describe a model's general nature. Given a set of models,
each fully described by this ontology in a computerized system (whether as a
database or a Web Ontology Language (OWL) system), the ontology allows for a
selection of models with characteristics that might be appropriate for a given
user.
The Model Metadata Ontology has also been used to improve the
DIME/PMESII VV&A Tool. The organizational
structure provided by the ontology improves the user's ability to find the
proper elements to ascribe to the system, model and modules and to display the
results in a meaningful manner.
If you arrived here using a keyword shortcut, you may use your
browser's "back" key to return to the keyword
distribution page.
 Return to Hartley's Projects Page
Return to Hartley's Projects Page

Return to Hartley's Projects Page